How AI-Generated Instruments Are Reshaping Music Production in 2025
AI-generated sounds are no longer fringe experiments; they’re shaping the way producers build songs in 2025. From synthetic orchestras to evolving textures, AI instruments can spark new creative directions and speed up production workflows. But alongside the excitement, questions remain: What are the risks, when should you use them, and how can tools like SoundID VoiceAI fit into your process?
This guide unpacks the opportunities and limitations of AI-generated instruments with a focus on how SoundID VoiceAI helps producers explore these sounds responsibly and creatively.
What Are AI-Generated Instruments?
AI-generated instruments are sounds created in real time by machine learning models rather than sampled from live recordings. Unlike traditional sample libraries or synthesizers, AI instruments can:
- Generate infinite variations of the same instrument.
- Morph between timbres on the fly.
- Respond to prompts or MIDI input with unique interpretations.
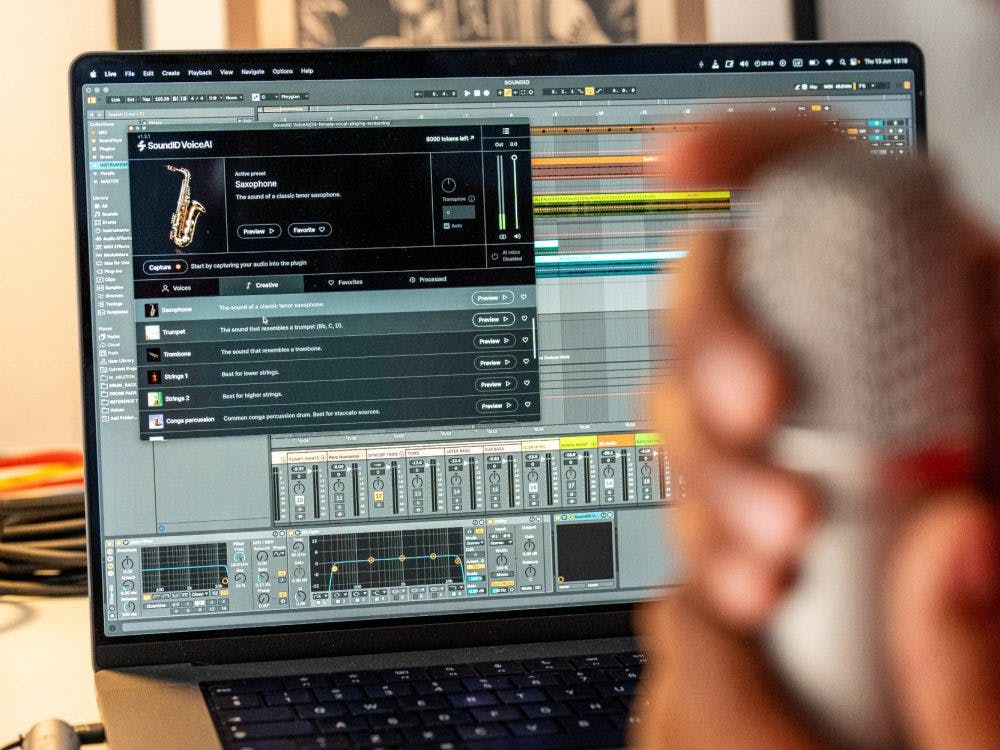
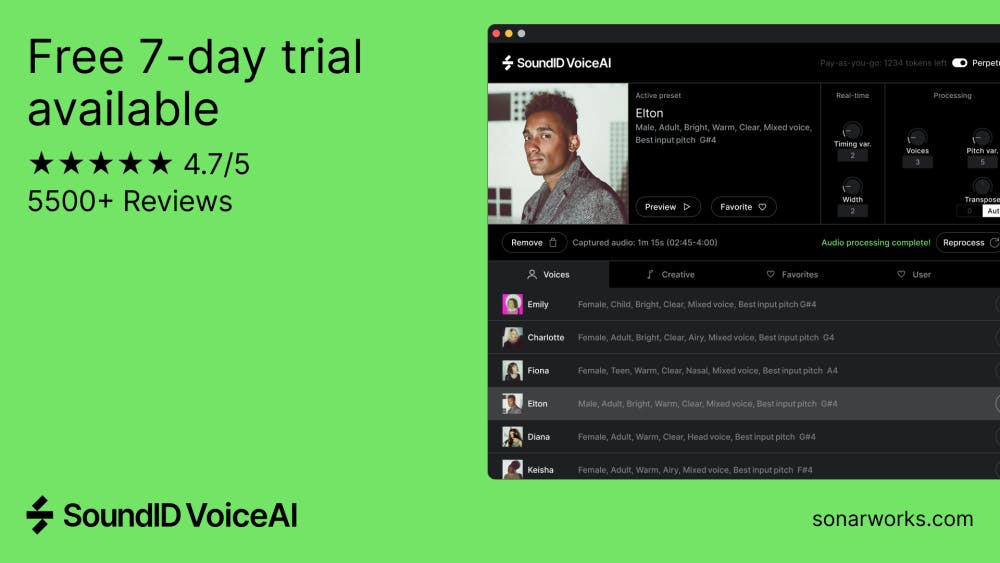
SoundID VoiceAI takes this concept further by letting you design custom vocal and instrumental textures, giving producers access to sonic palettes that feel both futuristic and usable in real-world tracks.
The Creative Potential of AI Instruments
Why are AI instruments gaining traction with producers?
- Rapid prototyping: Lay down draft tracks without session players.
- Endless variety: Explore unlimited takes and textures without resampling.
- Unique sounds: Break free from overused sample packs.
With SoundID VoiceAI, you can quickly create layered harmonies, hybrid voices, or instrument-like textures that push your arrangement into new creative territory.
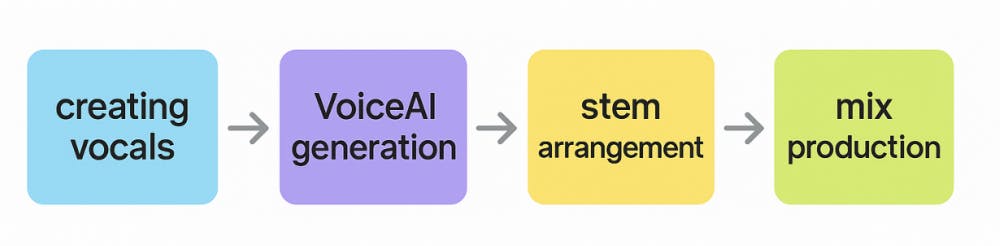
Technical & Workflow Considerations
AI-generated instruments sound inspiring, but they require a slightly different mindset than working with conventional VSTs:
- Consistency: Outputs may vary on each generation; save promising takes immediately.
- Integration: Export stems for editing in your DAW to keep flexibility.
- Balance: Use AI instruments alongside traditional layers for the best translation.
SoundID VoiceAI is designed with this workflow in mind, providing high-quality, DAW-ready stems so you can focus on creativity instead of technical cleanup.
Legal & Ethical Issues in 2025
AI-generated instruments also raise questions around ownership and rights. Producers need to consider:
- Copyright ownership: AI stems may not qualify as original works under current law.
- Licensing terms: Always check whether the plugin/service provider grants usage rights for commercial releases.
- Platform policies: Streaming platforms and labels are beginning to require disclosure of AI-generated material.
When to Use AI Instruments (and When to Avoid Them)
AI instruments can unlock new directions, but they’re not always the right fit.
Great fits:
- Songwriting drafts and demo production
- Electronic, experimental, and hybrid genres
- Layering with live recordings for unique textures
Caution needed:
- Genres where authenticity is expected (jazz, classical)
- Projects requiring exact instrument reproduction
- Contexts with strict client/legal requirements (film scoring, ad sync)
Future Outlook: AI Instruments Beyond 2025
In the coming years, AI instruments will continue to evolve:
- MIDI 2.0 integration for expressive real-time performance.
- Cross-modal tools that combine voice, instruments, and effects seamlessly.
- Hybrid workflows blending AI with traditional synthesis and sampling.
- Transparency standards that make it clear how AI models are trained and licensed.
As adoption grows, the producers who thrive will be those who treat AI not as a replacement for musicianship but as a powerful extension of their toolkit.
FAQs About AI-Generated Instruments
1. Are AI-generated instruments professional enough for release in 2025?
Yes. Tools like SoundID VoiceAI now deliver stems at commercial quality, already used in chart releases and film scoring.
2. Do I own the rights to music made with AI instruments?
It depends on the provider. With SoundID VoiceAI, you own the rights to your outputs, making them safe for commercial distribution.
3. How do AI instruments compare to sample packs or virtual instruments?
Unlike static samples or modeled VSTs, AI instruments generate unique variations every time offering originality and flexibility.
4. Can I release songs with AI instruments on Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube?
Yes. Platforms allow AI-generated content as long as you have clear licensing. SoundID VoiceAI outputs are fully usable for release.
5. What genres benefit most from AI-generated instruments?
Electronic, pop, hip-hop, and film scoring thrive with AI sounds. Acoustic-focused genres like jazz or classical may still rely on live musicians.
6. Will AI instruments replace producers or musicians?
No. AI is a tool that expands creative possibilities. Producers remain essential for arrangement, storytelling, and final production decisions.
Closing Thoughts
AI-generated instruments are more than a passing trend; they’re part of the future of music production. With SoundID VoiceAI, you can explore this frontier today, adding originality and flexibility to your creative process without worrying about licensing or technical bottlenecks.
Start your free 7-day trial of SoundID VoiceAI and see how AI-generated instruments can elevate your next project.